Inflight navigation problems are probably the largest source of problems for COPB candidates. Make sure that you use the operational data that is provided in the exam, plot the PZ’s / SZ’s on you map and take note of the company fuel policy that is provided.
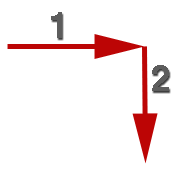
Plotting Positions
When plotting positions using a 6 figure group on a topographical chart like the 1:100,000 COWRA chart used in the examination the first 3 digits are used to obtain the position line across the page and the last 3 digits are used to obtain the position line down the page.
Practice position plotting exercises are available on a separate page.
Time and Distance Calculations
When completing time and distance exercises be sure that you convert to the correct units. Knots are nautical miles per hour and are not the same as kilometres per hour. To convert knots to km/hr multiply by 1.852. To convert nautical miles to kilometres multiply by 1.852. Conversion factors for the majority of units used in the aviation environment can be found in ERSA CON.
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is used by civil aviation. Time can be indicated by a four figure group, date and time can be indicated as a 6, 8 or 10 digit date / time group as indicated below. For most purposes a six figure group is used however, a 10 figure group is used for NOTAM and SUP.
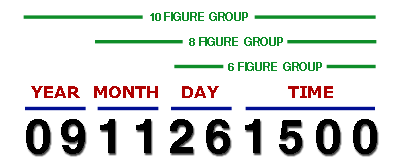
You should be able to convert from UTC to the common Australian time zones EST, AEDST, CST, WST and vice versa.
- Eastern Standard Time = UTC + 10 Hours
- Australia Eastern Summer Time = UTC + 11 Hours
- Central Standard Time = UTC + 9 1/2 Hours
- Western Standard Time = UTC + 8 Hours
Practice time and distance calculation exercises are available on a separate page.
Fuel Calculations
Spot Elevations and Contour Heights
Calculating Ground Speed
Determining Track Made Good (TMG)
Exercices
Position Plotting Exercises
Back to Exam Help Index
Technical data content credited to Mr Steve Griffin
